The accuracy of a vein scanner, also known as a vein finder or vein viewer, can vary based on several factors including the technology used, the specific device, and the conditions under which it is used. Here's a general overview:
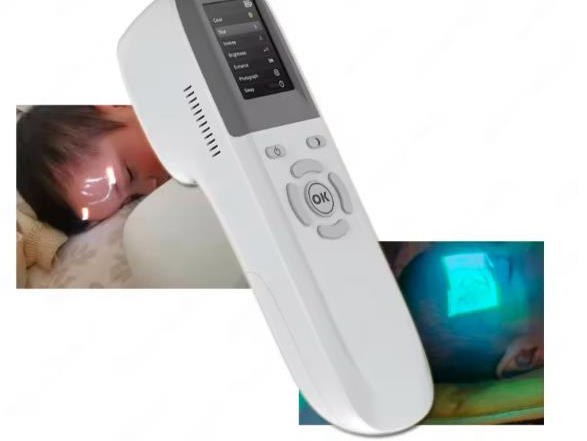
Technology
Infrared Light: Most vein scanners use near-infrared (NIR) light to detect veins. Hemoglobin in the blood absorbs the NIR light, making veins appear as dark lines on the device's screen.
Ultrasound: Some devices use ultrasound technology to visualize veins, providing real-time imaging that can be particularly useful for deeper veins.
Factors Affecting Accuracy
Skin Tone: Vein scanners can be more or less effective depending on the patient's skin tone. Darker skin tones may absorb more light, potentially reducing the contrast between veins and surrounding tissue.
Vein Depth: The depth of the veins can impact accuracy. Superficial veins are easier to detect, while deeper veins may be more challenging.
Patient Hydration: Well-hydrated patients typically have more prominent veins, which are easier to detect.
Body Fat: Higher levels of subcutaneous fat can make it more difficult to visualize veins.
Accuracy Metrics
Sensitivity: Refers to the device's ability to correctly identify the presence of a vein. High sensitivity reduces the likelihood of missing a vein.
Specificity: Refers to the device's ability to correctly identify areas without veins. High specificity reduces the likelihood of false positives.
Practical Use
Clinical Setting: In a controlled clinical setting, vein scanners can achieve high accuracy, often identifying veins with over 90% success.
Field Use: In more variable conditions, such as emergency settings or with less ideal lighting, accuracy might decrease.
Benefits
Improved Success Rates: Increased accuracy in vein detection can improve the success rate of venipuncture and IV insertions, reducing patient discomfort and procedure time.
Reduced Complications: Accurate vein identification helps in minimizing complications like hematomas and infections.
Limitations
Cost and Accessibility: High-quality vein scanners can be expensive, potentially limiting their use in some settings.
Training: Proper training is required to use the devices effectively, which can be a barrier in some healthcare environments.
Overall, modern vein scanners are quite accurate and provide significant benefits in clinical practice, especially when used under optimal conditions and by trained professionals.